Blog
Vision Gallery Blog
Vision Gallery Blog is your trusted source for informative articles, expert insights, and valuable tips related to eye health and vision care. Explore a wealth of knowledge on topics ranging from eye conditions, vision correction options, to maintaining optimal eye wellness. Stay informed and prioritize your eye health with our engaging and educational blog content.
article_category: eye surgery co-management
article_category: products
article_category: vision therapy
article_category: dogs
article_category: technology
article_category: general
article_category: eye health
article_category: aesthetics
article_category: services
article_category: faqs
article_category: exotic
article_category: large animal
article_category: contact lenses
article_category: surgical procedures
article_category: health
article_category: psychiatry
article_category: conditions
article_category: restorative
article_category: preventative
article_category: cats
article_category: eyeglasses
article_category: ocular disease management
[]
Flowbite is an open-source library of interactive components built on top of Tailwind CSS including buttons, dropdowns, modals, navbars, and more.
Check out this guide to learn how to get started and start developing websites even faster with components on top of Tailwind CSS.
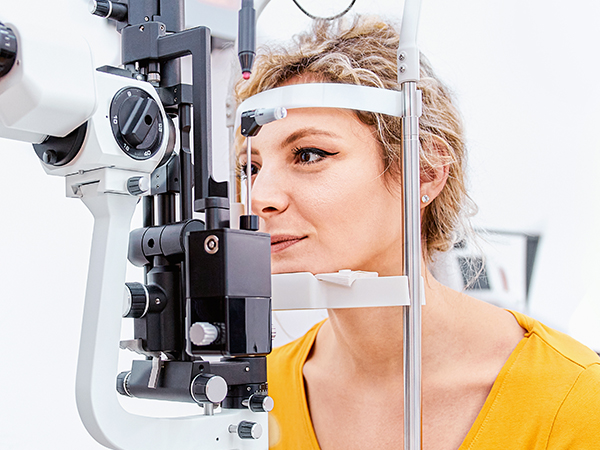
All Eye Care Services
Find personalized eye care excellence with our comprehensive services. From eye exams to advanced diagnostics, trust us for all your vision needs.

Keep In Touch
For non-urgent questions or to learn more about our services, contact us today!
Optical Services
Eyecare Services
Contact Info
Hours of Operation
- Monday 9:00am - 5:00pm
- Tuesday 10:00am - 6:00pm
- Wednesday 9:00am - 5:00pm
- Thursday 9:00am - 5:00pm
- Friday 9:00am - 5:00pm
- Saturday Closed
- Sunday Closed
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
- Sunday
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
- Sunday
© 2026 Vision Gallery. All rights Reserved - Accessibility Statement - Privacy Policy - Sitemap

