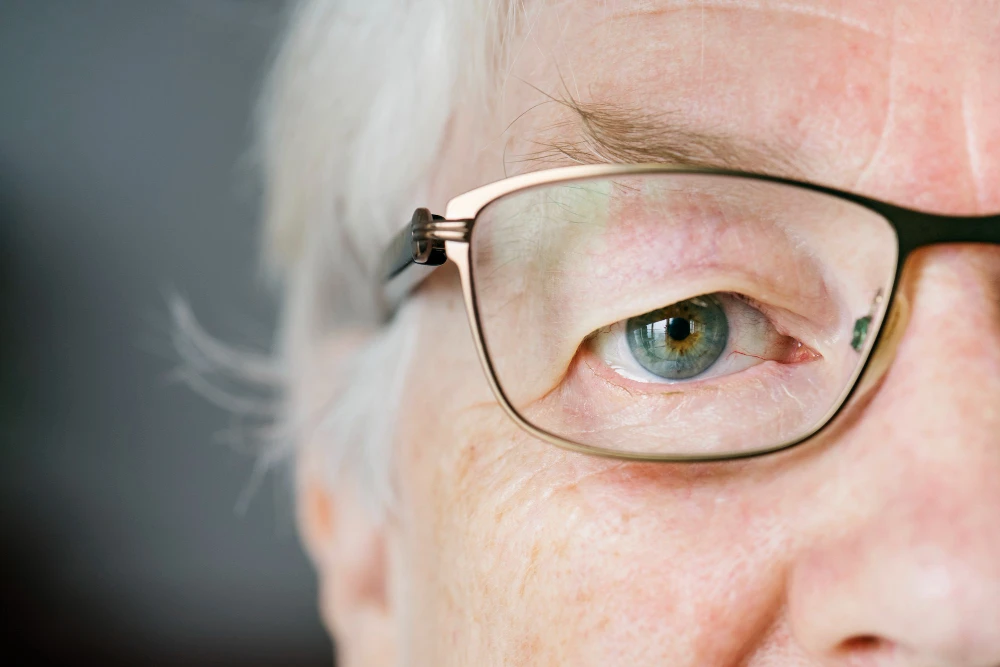
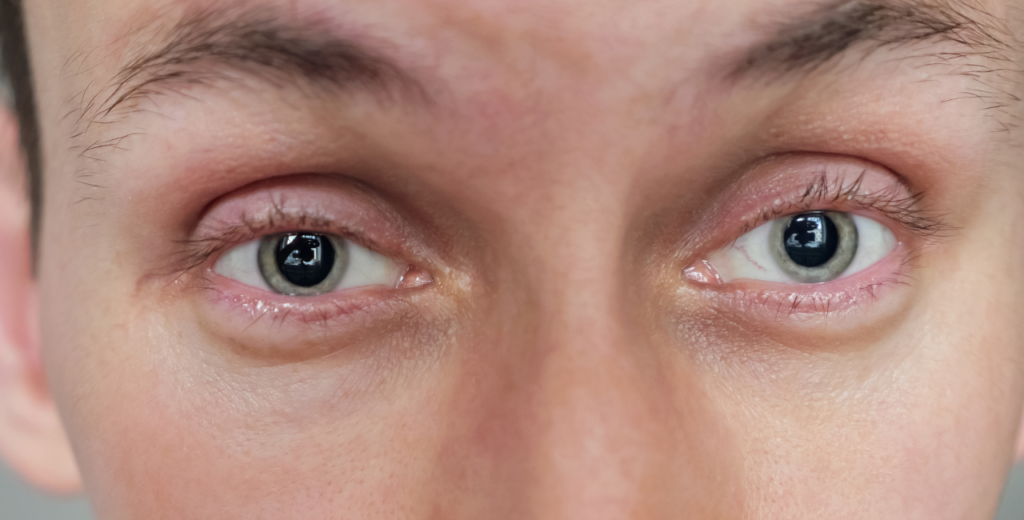
Thyroid Eye Disease (TED) is an autoimmune condition that affects the tissues around the eyes, often leading to eyelid retraction. TED is commonly associated with Graves’ disease, an autoimmune disorder that impacts the thyroid and eye muscles. This condition not only alters appearance but can also cause discomfort, dryness, and even vision issues. A comprehensive eye exam is essential for diagnosing TED, as it helps to assess the extent to which the eye is affected and monitor any vision changes. Understanding the causes and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
What Causes Eyelid Retraction?
Eyelid retraction occurs when the upper eyelid is pulled too high or the lower eyelid is pulled too low. This can result from:
Inflammation and Swelling
TED leads to inflammation, which can cause the muscles around the eyes to tighten and pull the eyelids back. This inflammation can also make the eyes feel dry, irritated, and more exposed to environmental factors. As a result, individuals may experience persistent discomfort, making everyday activities more challenging. Over time, if left untreated, the inflammation can cause long-term damage to the eyelid structure and function.
Fibrosis and Scarring
Over time, prolonged inflammation can cause scarring in the eyelid muscles. Scarred tissues become less flexible, making it difficult for the eyelids to return to their natural position. This scarring can also create a pulling sensation, leading to further complications in eye movement and appearance. In severe cases, the scarring may necessitate surgical intervention to correct the structural changes and restore normal eyelid function.
Overactive Thyroid Hormones
Hyperthyroidism can contribute to muscle tightening, worsening eyelid retraction. This hormonal imbalance can accelerate the progression of TED and lead to additional eye-related complications. Managing thyroid levels effectively can play a crucial role in controlling the severity of symptoms. Without proper regulation, the overactive thyroid may exacerbate inflammation and increase the risk of long-term eye damage.
Symptoms of Retracted Eyelids
Recognizing the symptoms early can help in managing the condition effectively. Common symptoms include:
Excessive Eye Exposure
White part of the eye is more visible, giving the eyes a more pronounced or startled appearance. This can contribute to eye strain and increased light sensitivity. The excessive exposure can also heighten the risk of eye infections due to a lack of adequate protection from external elements.
Dryness and Irritation
Eyes may feel gritty, watery, or excessively dry due to increased exposure to air and reduced blinking frequency. This can lead to discomfort and a burning sensation in the eyes. Prolonged dryness can further contribute to vision disturbances and make it difficult to wear contact lenses comfortably.
Light Sensitivity
Increased discomfort in bright environments, making it difficult to go outside without sunglasses or function comfortably under artificial lighting. People with severe light sensitivity may find it challenging to perform daily tasks such as driving, reading, or working on screens for extended periods.
Difficulty Closing Eyes Fully
This can lead to corneal damage over time as the eyes are unable to retain moisture properly, increasing the risk of infections and ulcers. When the eyes remain partially open during sleep, it can exacerbate dryness and increase discomfort upon waking.
Bulging Eyes (Proptosis)
The eyes may appear pushed forward due to swelling in the orbital tissues, creating an unnatural protruding look that may worsen with time. In extreme cases, proptosis can lead to visual disturbances, such as double vision or difficulty focusing on objects at different distances.
Treatment Options for Fixing Retracted Eyelids
There are several effective treatment options, ranging from non-surgical to surgical interventions.
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
For mild cases of eyelid retraction, non-surgical treatments may be beneficial:
Lubricating Eye Drops and Ointments
Helps prevent dryness and irritation by keeping the eyes moist. These can also act as a protective barrier against environmental irritants. Regular application of lubricants can significantly improve comfort and reduce the risk of corneal damage over time.
Steroid Therapy
Reduces inflammation in the eye tissues, helping to alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. However, prolonged steroid use requires medical supervision due to potential side effects. These medications should be used under strict medical guidance to avoid complications such as increased eye pressure or cataracts.
Botox Injections
Can temporarily relax tight muscles to lower the upper eyelid, offering a minimally invasive solution for mild retraction cases. Results typically last for a few months before requiring additional treatment. This treatment is often used as a bridge before considering surgical interventions for long-term correction.
Thyroid Management
Controlling thyroid hormone levels can prevent further worsening of symptoms. Endocrinologists may prescribe medication to balance hormone levels, slowing the progression of TED. A well-managed thyroid condition plays a vital role in reducing inflammation and minimizing eye-related complications.
2. Surgical Solutions for Eyelid Retraction
For moderate to severe cases, surgery may be necessary to restore a natural eyelid position:
Eyelid Lengthening Surgery
Adjusts the muscle and skin to lower the upper eyelid or raise the lower eyelid. This procedure restores a more natural eye appearance and improves eye closure. Proper post-surgical care is essential to ensure a smooth recovery and avoid complications such as scarring or asymmetry.
Orbital Decompression Surgery
Reduces the pressure on eye tissues, helping improve eyelid positioning. This procedure involves removing excess fatty tissue or bone to create more space for the swollen eye muscles. Patients undergoing this surgery typically experience significant relief from symptoms and an improved aesthetic appearance.
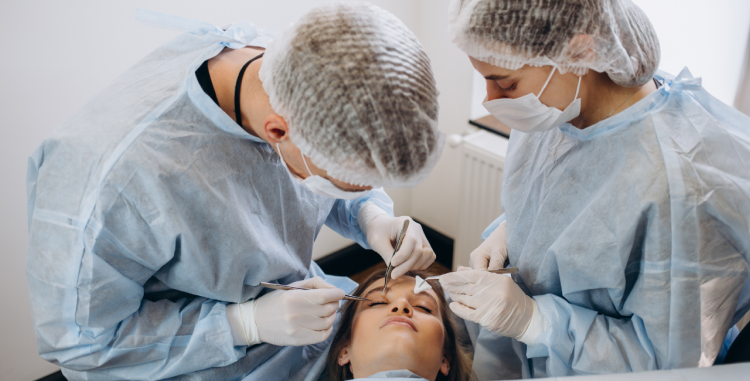
Fat Grafting or Dermal Fillers
Adds volume to the lower eyelids, improving symmetry and function. These treatments provide a non-invasive way to enhance appearance and comfort while reducing eye exposure. Fillers can offer a temporary solution, but surgical intervention may be required for more severe cases.
Upper Eyelid Surgery
Focused on repositioning the upper eyelid for a more natural and functional appearance. This surgery helps address issues such as eyelid drooping or retraction that affects vision and aesthetics. Proper evaluation is essential to determine the best approach for each patient.
Lower Eyelid Surgery
Addresses concerns like eyelid retraction and exposure of the eyeball, which can lead to irritation and discomfort. This surgery helps restore the natural position of the lower eyelid and improves overall eye function, providing both aesthetic and functional benefits.
Recovery and Post-Treatment Care
Proper post-treatment care ensures the best results and prevents complications:
Follow Medication Instructions
Adhere to prescribed medications, including anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics, to support healing and prevent infections. Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment as necessary.
Use Prescribed Eye Drops
Keeping the eyes lubricated reduces irritation and promotes recovery by maintaining proper moisture levels. It is essential to use eye drops consistently to prevent dryness-related complications.
Avoid Rubbing Your Eyes
Touching or rubbing the eyes can worsen symptoms and interfere with healing, increasing the risk of complications. Using protective eyewear can help minimize accidental eye contact.
Limit Exposure to Environmental Irritants
Wind, dust, and bright light can exacerbate symptoms. Wearing sunglasses and using protective measures can help minimize discomfort. Keeping a humidifier in your living space can also help maintain moisture levels and reduce dryness.
Attend Follow-Up Appointments
Regular check-ups ensure proper healing and allow for adjustments in treatment if necessary. If new symptoms arise, seek medical advice promptly to prevent complications.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you experience worsening symptoms, pain, or difficulty closing your eyes, consult an eye specialist immediately. Delayed treatment can lead to serious complications, including corneal damage and vision impairment.
At Vision Gallery, we specialize in evaluating and managing thyroid eye disease and eyelid retraction with state-of-the-art solutions tailored to your needs. Our expert team of optometrists provides thorough consultations and non-surgical treatment options to help restore your comfort and confidence.
Schedule a consultation today and take the first step toward healthier eyes!